The debate over sex education in schools has reached fever pitch, with battle lines drawn between those advocating for comprehensive programs starting as early as kindergarten and critics who believe such education corrupts young minds. But what does the science actually tell us? The research is overwhelmingly clear: comprehensive sex education (CSE) not only works—it's essential for protecting children and reducing harmful outcomes..
The Remarkable Benefits: What Research Reveals
Dramatic Reduction in Teen Pregnancy and STIs
The numbers don't lie. Comprehensive sex education reduces teen pregnancy rates by an astounding 50% compared to abstinence-only programs. States with comprehensive sex education consistently show the lowest teen pregnancy rates, while those emphasizing abstinence-only approaches see significantly higher rates.
A massive meta-analysis of 87 studies by UNESCO found that comprehensive sex education leads to:
Delayed sexual debut - teens wait longer before having sex
Fewer sexual partners when sexually active
Increased condom and contraceptive use by 40%
Reduced STI transmission rates by up to 30%
Lower rates of unprotected sex
Decreased risky behaviors like sex under the influence of alcohol
Enhanced Knowledge and Decision-Making Skills
Research consistently shows that CSE programs significantly improve students' sexual health knowledge and decision-making abilities. Students gain crucial understanding about:
Anatomy and reproductive health
Consent and healthy relationships
Communication and negotiation skills
Protection methods and contraception
Recognition of sexual abuse and exploitation
Protection Against Sexual Violence
One of the most compelling benefits is CSE's role in preventing sexual abuse and exploitation. Age-appropriate programs teach children about:
Body autonomy and personal boundaries
Identifying inappropriate touching
Trusted adults they can talk to
The difference between appropriate and inappropriate relationships
Studies show that 7.9% of boys and 19.7% of girls experience sexual abuse before age 18. Early education provides critical protective knowledge.
What Age-Appropriate Actually Means
Critics often misunderstand what "sex education" looks like for young children. Kindergarten CSE isn't about explicit sexual content - it's about foundational safety and relationship skills.
Elementary School (Ages 5-10)
Correct anatomical names for body parts
Personal boundaries and consent concepts using activities like hula hoops
Family diversity and different types of families
Identifying trusted adults for support
Basic puberty preparation starting around 4th grade
Middle School (Ages 11-14)
Detailed puberty education
Healthy relationship characteristics
Communication skills
Introduction to reproduction concepts
Personal safety and avoiding exploitation
High School (Ages 15-18)
Comprehensive sexual health information
Contraception methods and effectiveness
STI prevention and testing
Consent and sexual decision-making
Pregnancy options and parenting realities
The Concerning Downsides and Valid Criticisms
Despite overwhelming evidence supporting CSE, legitimate concerns exist that deserve consideration.
Implementation Challenges
Teacher Training Gaps: Many educators feel unprepared to deliver sex education effectively. Without proper training, even well-designed curricula can fail to achieve intended outcomes.
Quality Control Issues: Studies reveal massive inconsistencies between schools and regions. Some students receive comprehensive education while others get minimal or inadequate instruction, creating unequal protection.
Cultural and Religious Objections
Parental Rights Concerns: Many parents believe they should control when and how their children learn about sexuality. Religious families often prefer education that aligns with their values emphasizing marriage and abstinence.
Values Conflicts: Conservative religious groups argue that CSE undermines traditional family values and moral teachings. Some worry that discussing topics like sexual orientation and gender identity contradicts their beliefs.
Potential Risks of Poor Implementation
Age-Inappropriate Content: When programs aren't properly designed, children might be exposed to information that's developmentally inappropriate, potentially causing confusion or anxiety.
Premature Curiosity: Critics argue that introducing sexual concepts too early might increase children's curiosity and lead to experimentation. However, research consistently disproves this concern.
The Global Success Stories vs. US Struggles
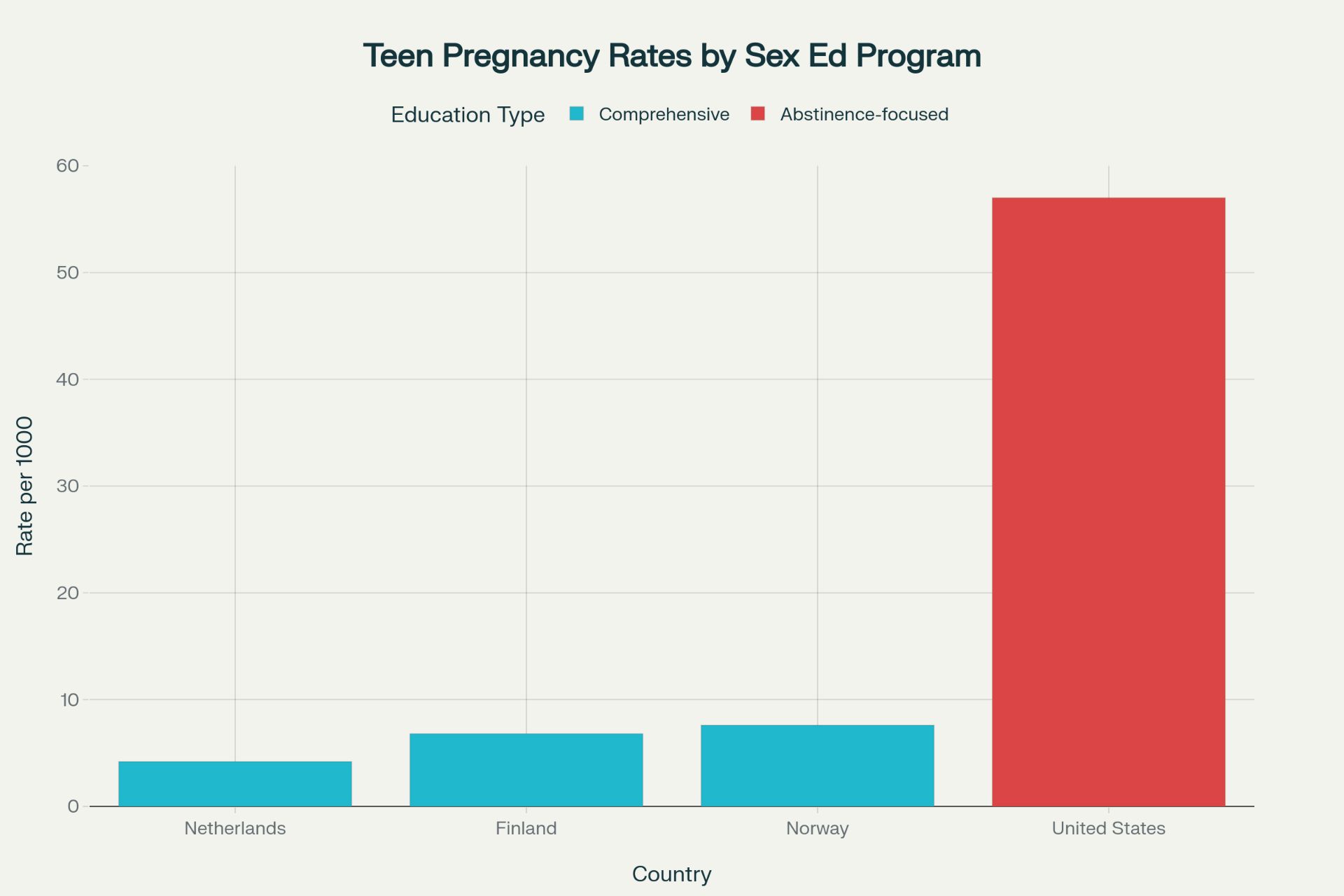
Countries with comprehensive sex education programs dramatically outperform the United States in sexual health outcomes.
The Netherlands: A Model of Success
The Dutch approach starts at age 4 with relationship and boundary education. Results are remarkable:
World's lowest teen pregnancy rates (4.2 per 1,000 teens)
90% of teens use contraception during first sexual encounter
Positive first sexual experiences reported by most teens
Low STI and HIV rates despite similar sexual activity timing to other countries
Nordic Excellence
Finland and Norway implement comprehensive programs with outstanding results:
Finland: 6.8 per 1,000 teen pregnancy rate
Norway: 7.6 per 1,000 teen pregnancy rate
Both countries emphasize positive sexuality and skill development
US Lagging Behind
Despite spending millions on abstinence-only programs, the United States shows:
57 per 1,000 teen pregnancy rate - dramatically higher than CSE countries
Higher STI rates among adolescents
Increased sexual risk behaviors in abstinence-only states
Why Abstinence-Only Approaches Fall Short
Multiple large-scale studies demonstrate that abstinence-only education is not just ineffective—it may actually increase harmful outcomes.
The Research Verdict
No delay in sexual initiation compared to comprehensive programs
No reduction in teen pregnancy rates
Higher STI transmission in abstinence-only regions
Reduced contraceptive knowledge when teens do become sexually active
Increased shame and guilt around normal sexual development
Information Gaps Create Dangers
When teens lack comprehensive sexual health information, they turn to unreliable sources like pornography and internet searches. This leads to:
Misconceptions about sex and relationships
Unrealistic expectations and behaviors
Increased risk-taking without protective knowledge
Delayed help-seeking for sexual health concerns
Addressing Parental Concerns Constructively
Research shows that even highly religious parents support most CSE topics when properly informed. Opposition typically stems from misunderstanding about age-appropriate content.
Building Family-School Partnerships
Successful programs involve parents through:
Clear communication about curriculum content and timing
Parent education sessions explaining age-appropriate approaches
Opt-out policies respecting family values while protecting all children
Home-school coordination reinforcing consistent messages
Respecting Cultural Differences
Effective CSE programs can be adapted to respect diverse cultural and religious values while maintaining core protective elements around:
Abuse prevention and safety
Basic anatomy and health information
Respect for others and healthy relationships
Critical thinking skills for media literacy
The Evidence-Based Path Forward
The research conclusion is unambiguous: comprehensive sex education starting in elementary school provides significant benefits with minimal risks when properly implemented.
Key Success Factors
Effective programs require:
Teacher training and ongoing support
Age-appropriate, evidence-based curricula
Community engagement and parental involvement
Quality assurance and program evaluation
Integration with broader health education
Addressing Implementation Challenges
To maximize benefits while minimizing concerns:
Invest in comprehensive teacher preparation
Develop clear quality standards and oversight
Create culturally sensitive adaptation options
Ensure consistent delivery across all schools
Provide ongoing program evaluation and improvement
The choice isn't whether to educate young people about sexuality—they're already receiving information from multiple sources, often unreliable ones. The question is whether schools will provide accurate, age-appropriate, protective education or leave children vulnerable to misinformation, abuse, and preventable health consequences.
The evidence overwhelmingly supports starting comprehensive sex education early. When implemented thoughtfully with proper training and community engagement, these programs protect children, reduce harmful outcomes, and build foundations for healthy relationships throughout life. The stakes are too high—and the benefits too substantial—to let ideology override evidence-based approaches that save lives and prevent suffering.



