Digital assessment has moved from contingency plan to core infrastructure, reshaping how schools, universities, and national testing bodies measure learning and gate admissions.
From Paper to Platform: Why Exams Went Digital
Scale and standardization: Centralized agencies can run uniform, high-stakes exams across geographies with consistent processes and auditing.
Speed and feedback: Auto-marking and structured workflows compress grading cycles and return results faster.
Integrity by design: Browser lockdown, identity checks, and proctoring deter misconduct and preserve trust.
Accessibility and flexibility: Remote delivery and multimodal question types better fit diverse learners.
Inside Modern Online Exam Systems
Authoring and item banks: Educators build question pools, reuse items, and assemble forms in minutes.
Auto-grading engines: Objective items (MCQ, numeric, regex, hotspots) grade instantly; rubrics streamline partial credit for constructed responses.
Secure delivery: Exam keys, no student accounts, timed windows, and environment controls create a focused test session.
Proctoring layers: Options span live proctors, AI flags, and secure mode to match risk and budget.
Evidence capture: File uploads, equation editors, and embedded tools (e.g., graphing) preserve student work for transparent scoring.
Analytics: Item difficulty, discrimination, and distractor analysis inform remediation and future test design.
Case Snapshot: Classroom to Campus
K–12 and teacher-led testing: Platforms designed by former educators emphasize setup speed, clean interfaces, and practical features like reusable item banks, equation editors, and integrated graphing—useful for math and sciences.
University-scale administration: Exam services units coordinate e-services, question banks, and unfair-means (UFM) workflows across faculties for consistent policy enforcement.
National high-stakes exams: Independent testing agencies conduct uniform entrance tests with standardized answer keys, OMR scans, and result publication at massive scale.

The Security Stack: Preventing Cheating Without Breaking Usability
Secure browser/lockdown: Disables switching, copy-paste, and external sites during the exam session.
Identity and environment checks: Exam keys, ID verification, and optional room scans for higher stakes.
Proctoring spectrum: From unproctored with audit logs to AI-assisted review to live invigilators.
Content security: Randomization, multiple form variants, time windows, and question shuffling.
Data integrity: Timestamps, network resilience, and autosave to prevent loss and disputes.
Designing Better Assessments (Not Just Digitizing Paper)
Align items to outcomes: Map every question to a skill or standard to ensure coverage and fairness.
Vary modalities: Mix objective items with short reasoning prompts and file-uploaded work for depth.
Use integrated tools judiciously: Calculators, graphing, and equation editors should match learning goals, not shortcut them.
Pilot and analyze: Run small pilots; use item statistics to retire, revise, or reuse.
Balance security vs. experience: Choose the least intrusive controls that still uphold integrity.
How to Choose a Platform
Use case fit: Classroom quizzes vs. department finals vs. national entrance tests require different security and scale profiles.
Authoring power: Look for rich item types, reusable libraries, and fast assembly.
Integrity controls: Ensure configurable lockdown, proctoring options, randomized delivery.
Student experience: Minimal friction—no accounts where possible, clear UI, accessibility features.
Ecosystem integration: LMS, SSO, and data export for compliance and analytics.
Support and reliability: Uptime SLAs, clear incident response, and educator-centric support.
Real-World Examples at a Glance
Educator-first platform: Emphasizes ease of use, no student accounts, exam keys, reusable question banks, auto-marked items, and math-friendly tooling like equation editors and integrated graphing.
University examination wing: Centralizes services including question banks and UFM portals to standardize policy and student access across campuses.
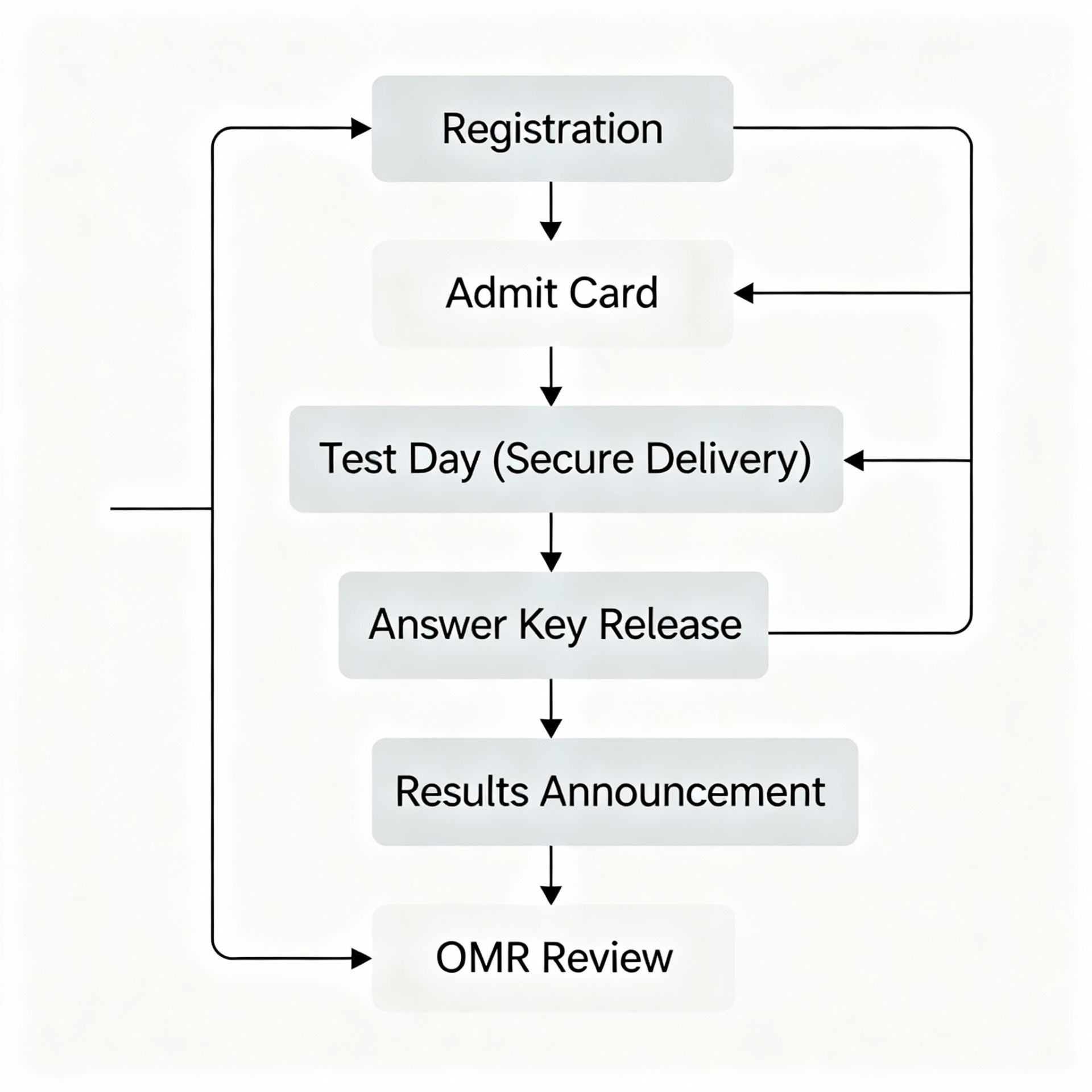
National testing agency: Runs uniform entrance tests (e.g., NEET-UG), publishes provisional and final answer keys, and provides OMR image access and result ranks at national scale.
Examination services hub: Lists active and upcoming public examinations and provides candidate information channels for scheduling and administration.
The Future: Hybrid Integrity and Faster Feedback Loops
Privacy-aware proctoring: Shift toward explainable AI flags, on-device processing, and consent-first policies.
Adaptive pathways: Multi-form, algorithmically assembled tests that personalize difficulty while preserving fairness.
Instant transparency: Same-day provisional keys, candidate response views, and rapid challenge windows to increase trust.
Competency credentials: Micro-assessments and badges complement summative exams for continuous learning records.



