Whey protein has evolved from a niche bodybuilding supplement into a mainstream nutritional powerhouse that's reshaping how we approach fitness, weight management, and overall health. With the global whey protein market exploding from $22.6 billion in 2025 to a projected $46.6 billion by 2035, it's clear that this isn't just another fleeting wellness trend. But what makes whey protein so special, and more importantly, which type should you be adding to your shaker bottle?
What Exactly Is Whey Protein?
Let's start with the basics. Whey protein is a mixture of proteins extracted from whey, the liquid byproduct that separates from milk during cheese production. Remember that watery layer floating on top of your yogurt? That's whey. What cheesemakers once discarded as waste has now become one of the most valuable nutritional supplements on the planet.
Milk contains two main protein types: casein (80%) and whey (20%). While casein digests slowly, whey is a complete protein packed with all nine essential amino acids your body can't produce on its own. This makes it incredibly efficient for muscle protein synthesis and recovery.
The Three Musketeers: Types of Whey Protein
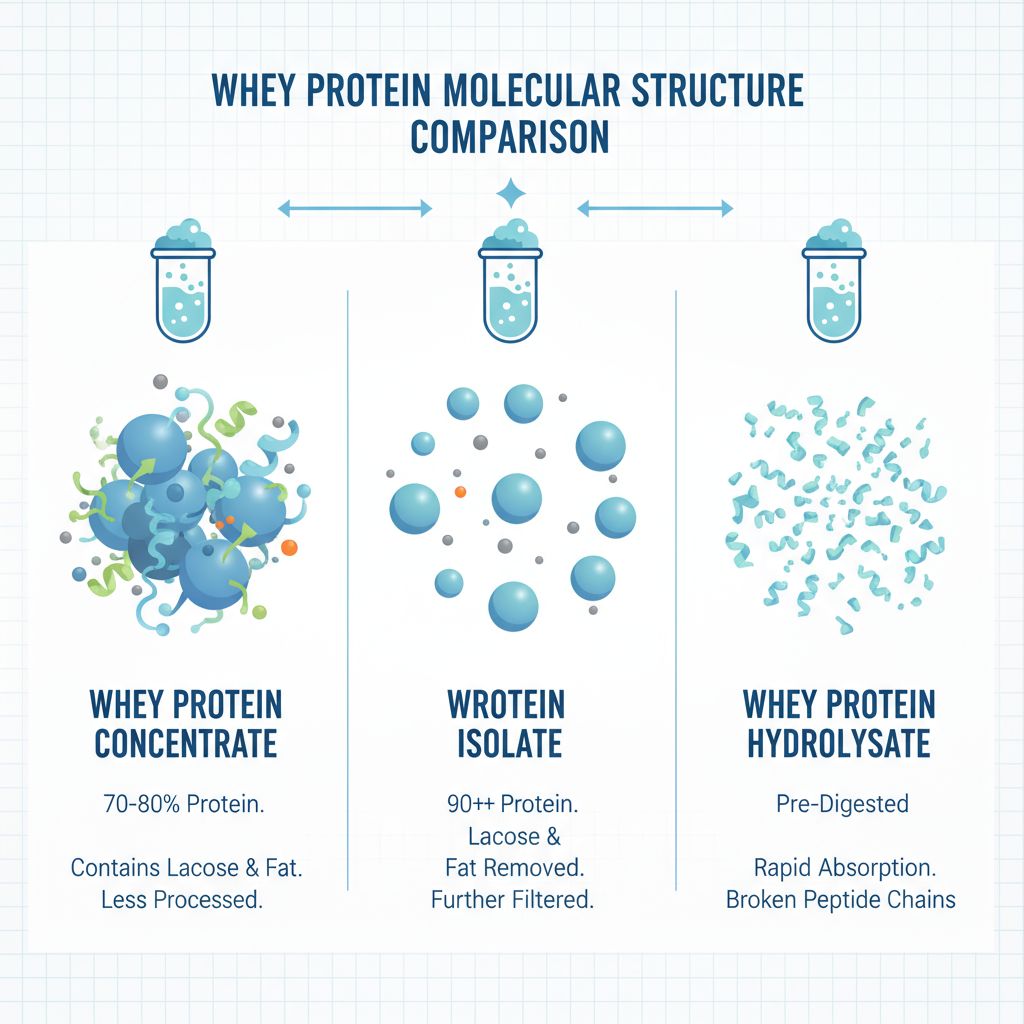
Not all whey proteins are created equal. Understanding the three main types can save you money and help you choose the right supplement for your goals.
Whey Protein Concentrate (WPC)
WPC is the most affordable and popular option, containing 70-80% protein with moderate amounts of lactose and fat. The protein concentration can vary from 50-90%, making it ideal for beginners, muscle builders, and those looking to gain weight. Because it undergoes less processing, WPC retains more naturally occurring nutrients like immunoglobulins and lactoferrin, which support immune health.
Best for: General fitness enthusiasts, muscle gain, budget-conscious buyers
Whey Protein Isolate (WPI)
WPI is the refined powerhouse, boasting 90-95% protein content with less than 1% lactose and minimal fat. Through additional filtration, manufacturers remove most non-protein components, resulting in a leaner, faster-absorbing product. This makes WPI perfect for those with lactose intolerance or anyone focused on cutting body fat while preserving muscle.
Best for: Lactose-sensitive individuals, cutting phases, lean muscle development
Whey Protein Hydrolysate (WPH)
The premium tier of whey proteins, WPH contains around 99% protein. Through a process called hydrolysis, protein molecules are broken down into smaller peptides, making it the fastest-absorbing form available. This pre-digestion process also reduces allergen potential and makes it incredibly water-soluble.
Best for: Rapid recovery, sensitive digestion, elite athletes, cancer patients requiring nutritional support
The Science-Backed Benefits That Actually Matter
Muscle Growth and Recovery
The muscle-building reputation of whey protein isn't just gym bro mythology—it's backed by solid science. Whey is particularly rich in leucine, a branched-chain amino acid (BCAA) that triggers muscle protein synthesis through the mTOR pathway. Research shows that whey protein, especially isolate, stimulates myofibrillar muscle protein synthesis more effectively than concentrate due to its rapid digestion and absorption.

A comprehensive meta-analysis examining 14 randomized controlled trials found that participants combining whey protein with resistance training gained an average of 2.24 kg of lean body mass. The benefits are especially pronounced for novice and recreational athletes, though advanced lifters may need higher doses (1.4-2.0 g/kg body weight daily) to see continued gains.
Weight Loss and Fat Reduction
Here's where whey protein gets really interesting for non-athletes. A groundbreaking 12-week study revealed that participants consuming specialized whey protein lost significantly more body fat compared to controls—2.81 kg versus 1.62 kg—while preserving lean muscle mass. The fat-to-lean loss ratio was dramatically better in the whey group: 3.75 versus 1.05.
Why does this work? Protein has a high thermic effect, meaning your body burns more calories digesting it compared to fats or carbs. Plus, whey increases feelings of fullness, naturally reducing overall calorie intake throughout the day.
Blood Pressure, Blood Sugar, and Beyond
The benefits extend well beyond the gym. Studies have identified associations between whey protein consumption and:
Lowered blood pressure in hypertensive individuals
Improved blood sugar management for type 2 diabetics
Reduced inflammation through bioactive peptides
Enhanced immune function via immunoglobulins and lactoferrin
Antioxidant support by boosting glutathione production
The Real Talk: Side Effects and Risks
Let's not sugarcoat it—whey protein isn't perfect for everyone. Here's what you need to know about potential downsides.
Digestive Issues
The most common complaints involve bloating, gas, cramping, and diarrhea, typically affecting those with lactose intolerance. Since lactose intolerance affects up to 65% of people worldwide, this is a significant consideration. Switching to whey isolate (which contains minimal lactose) or plant-based alternatives usually resolves these issues.
Concerns for Kidney and Liver Health
This is where the evidence gets murky. While high-protein diets increase the kidneys' filtration workload, a review of 74 studies concluded there's no reason to restrict protein intake in healthy individuals. However, people with existing kidney or liver conditions should consult healthcare providers before supplementing.
Notably, taking excess whey protein without exercising can lead to liver inflammation and increase the risk of serious liver injury. The message is clear: supplements work best when combined with actual training.
Other Potential Side Effects
Research has linked chronic protein supplementation to:
Increased acne due to insulin-like growth factor-1 and hormonal effects
Mood changes as BCAAs compete with tryptophan, potentially reducing serotonin synthesis
Altered gut microbiota from amino acid fermentation in the colon
Allergic reactions in children intolerant to cow's milk
Whey vs. Plant Protein: The Great Debate
With plant-based diets surging in popularity, how does whey stack up against alternatives like pea, soy, and rice protein?

Factor | Whey Protein | Plant Protein |
|---|---|---|
Amino Acid Profile | Complete (all 9 essential amino acids) | Often incomplete unless blended |
BCAA Content | ~26% (higher leucine) | 18-19% |
Absorption Speed | Fast | Slower |
Digestibility | Easily absorbed | Less easily absorbed |
Lactose Content | Contains lactose | Lactose-free |
Environmental Impact | Higher carbon footprint | Significantly lower |
Taste/Texture | Creamy and smooth | Earthy and grittier |
Price | Generally lower | Often more expensive |
Diet Suitability | Not vegan/dairy-free | Vegan, vegetarian friendly |
Bottom line: Whey edges out plant protein for muscle building due to superior amino acid profiles and faster absorption. However, plant proteins offer sustainability benefits, suit dietary restrictions, and provide additional fiber and phytonutrients.
How to Choose the Right Whey Protein
With hundreds of brands flooding the market, here's your expert checklist:
1. Match Type to Goal
Building muscle/bulking: WPC or WPI (20-30g protein per serving)
Cutting/fat loss: WPI (minimal carbs and fats)
Sensitive digestion: WPH or WPI
Budget-conscious: WPC
2. Check the Label
Look for products with:
90%+ protein content for isolates
Minimal additives (avoid artificial sweeteners, excessive fillers)
20-30 grams protein per serving
Third-party certification (NSF, Informed-Sport, USP)
Complete amino acid profile with high BCAAs
3. Top Indian Brands for 2025
Based on market analysis and user reviews, here are the leading options in India:
Optimum Nutrition Gold Standard: ₹3,000-3,500/kg, 24g protein, globally trusted
MuscleBlaze Biozyme: ₹2,200-2,500/kg, enhanced absorption
Dymatize ISO100: ₹3,500-4,000/kg, pure isolate, zero carbs
MyProtein Impact Whey Isolate: Premium quality, multiple flavors
BBI Whey Protein: ₹2,699/kg, 25g protein, excellent value for Indian market
4. Consider Your Lifestyle
If you're lactose intolerant, WPI or plant-based proteins are your friends. Vegans should skip whey entirely and opt for blended plant proteins that provide complete amino acid profiles. Environmental concerns? Plant proteins win hands down with significantly lower carbon emissions and water usage.
When to Take Whey Protein: Timing Strategies
The "anabolic window" myth—that you must consume protein within 30 minutes post-workout—has been largely debunked. Recent research shows the benefits extend up to 24 hours after training. Here's what actually matters:
Post-Workout Recovery
Consuming whey after exercise accelerates muscle repair and promotes growth. This remains the most popular timing strategy, especially for strength and power athletes.
Pre-Workout Energy
Taking whey before training (if you haven't eaten for several hours) prevents muscle catabolism during intense sessions.
Between Meals
Spacing protein intake throughout the day maintains steady amino acid levels, supporting continuous muscle protein synthesis.
Upon Waking
A morning protein shake breaks the overnight fast, halts muscle catabolism from sleeping, and restarts anabolic processes.
Before Bed
Consuming 40 grams of protein before sleep maximizes overnight muscle development and recovery—particularly beneficial for older adults and serious athletes. Consider slower-digesting casein for this timing rather than fast-absorbing whey.
The verdict: Total daily protein intake (0.8-2.2 g/kg body weight depending on activity level) matters more than precise timing.
Delicious Ways to Use Whey Protein
Forget boring shakes. Here are creative recipes to keep your protein intake exciting:
The Perfect Fruity Breakfast Smoothie
250ml milk
1 scoop whey protein
1 banana
Dollop Greek yogurt
Handful frozen berries
1,000-Calorie Mass Gainer Smoothie
1½ cups whole milk
2 scoops whey protein
1 cup oats
2 tbsp peanut butter
1 banana
1 tbsp honey
½ cup frozen strawberries
Apple Cinnamon Hemp Heart Smoothie
1½ cups whole milk
2 small apples, sliced
⅓ cup rolled oats
2 tbsp almond butter
2 tbsp hemp hearts
1 tsp vanilla extract
Cinnamon to taste
Beyond smoothies, you can mix whey into oatmeal, yogurt, pancake batter, protein bars, and even baked goods like muffins.
The Market Explosion: Why Everyone's Talking About Whey
The numbers tell a compelling story. The global whey protein market is experiencing explosive growth with a 7.5% CAGR. In India specifically, the market is projected to grow from $180 million in 2024 to $240 million by 2033.
What's driving this surge?
Rising fitness culture especially in China (9.2% growth) and India (8.7% growth)
Clean label trends pushing minimal processing and natural ingredients
Mainstream adoption as whey moves from supplement aisles to everyday grocery formats
Functional food integration in protein bars, beverages, and breakfast foods
Increasing health awareness particularly in urban centers
Clear whey protein—a transparent, juice-like alternative to traditional creamy shakes—is emerging as a major trend in 2025. It offers the same protein benefits with a refreshing, light texture that appeals to consumers who dislike thick shakes.
Your Action Plan: Getting Started With Whey
Here's your step-by-step approach to integrating whey protein effectively:
Step 1: Calculate your protein needs (0.8g per kg body weight for sedentary; up to 2.2g per kg for athletes)
Step 2: Choose your type based on goals, budget, and digestive tolerance
Step 3: Start with one serving (20-30g) daily and assess tolerance
Step 4: Time consumption based on convenience—consistency beats perfection
Step 5: Track results over 4-6 weeks (strength gains, body composition changes, recovery improvements)
Step 6: Adjust dosage and timing as needed
The Final Scoop
Whey protein stands as one of the most researched, effective, and versatile nutritional supplements available today. Whether you're chasing muscle gains, supporting weight loss, or simply trying to hit your daily protein targets more conveniently, whey delivers proven results backed by decades of scientific research.
The key is matching the right type to your specific needs. WPC offers affordability and natural nutrients for general use. WPI provides lean protein for cutting phases and lactose-sensitive individuals. WPH delivers rapid absorption for elite performance and recovery.
But remember—supplements are exactly that: supplemental. No amount of premium whey powder will compensate for inconsistent training, poor sleep, or a fundamentally flawed diet. Use whey as a tool to support your efforts, not replace them.
With the market projected to double within the next decade, innovation in flavors, formulations, and functional applications will only expand your options. The future of whey protein looks bright, transparent (hello, clear whey!), and more accessible than ever before.
So grab your shaker bottle, choose your whey wisely, and fuel your fitness journey with science-backed nutrition. Your muscles—and your future self—will thank you.



